Ross Sea Region MPA
Established in 2016, the Ross Sea Region marine protected area covers an area of pristine polar wilderness more than three times the size of California, making it the largest marine park on the planet.
Welcome to the Ross Sea
ROSS SEA region MPA
The Ross Sea is one of the most-studied ocean ecosystems in Antarctica, and an important living laboratory for south polar research.
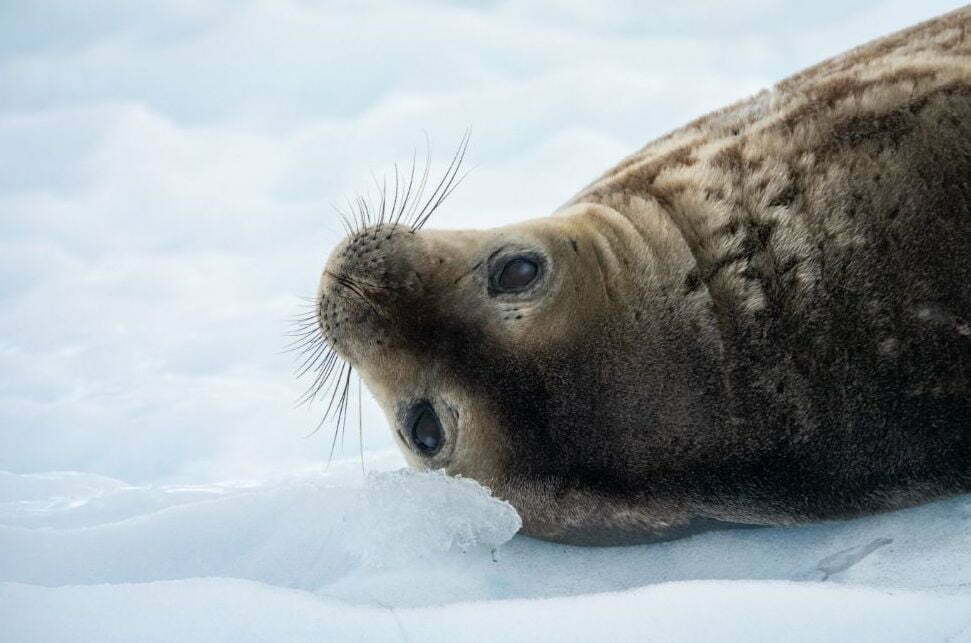
The Ross Sea Shelf is one of the most productive parts of the Southern Ocean, supporting more than 30% of the world’s Adélie penguins, around 30% of the Antarctic petrels, half the Ross Sea orcas and one quarter of all emperor penguins. More than half of the world’s South Pacific Weddell seals live there year round.
The Ross Sea also contains breeding grounds and habitats for Antarctic toothfish, rare and vulnerable benthic species, such as unique sponges that can live for 500 years, and other areas important for ecosystem integrity.
The Ross Sea Region MPA
ROSS SEA region MPA
The Ross Sea Region marine protected area (MPA) was initially proposed by the U.S. and New Zealand in 2012.
The Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources approved the MPA during its 35th annual meeting, which ended on October 28, 2016, in Hobart, Australia. The decision was unanimously supported by representatives of 24 countries and the European Union, and is a great achievement for the protection of the Southern Ocean.
The MPA entered into force on 1 December 2017 and will be in place for 35 years.

The Ross Sea Region MPA
ROSS SEA region MPA
The Ross Sea Region MPA covers a surface area of 600,000 square miles (1.55 million square kilometers), more than three times the size of California. This does not include the area underneath the floating Ross Ice Shelf, which increases the protected area to over 800,000 square miles (2.09 million square kilometers).
The majority of the Ross Sea Region MPA is fully protected under a General Protection Zone (GPZ). Around 72% of the MPA is a no-take zone, excluding areas under ice shelves. There is also a Special Research Zone (SRZ), which allows for some fishing of toothfish but not krill, and a Krill Research Zone (KRZ) which allows for some fishing of krill but not toothfish.
“[This] agreement is a turning point for the protection of Antarctica and the Southern Ocean. This is important not just for the incredible diversity of life that it will protect, but also for the contribution it makes to building the resilience of the world’s ocean in the face of climate change.”
Chris Johnson, Ocean Science Manager, WWF Australia
An uneasy compromise
ROSS SEA region MPA
The proposed Ross Sea Region MPA was supported by the best available science and endorsed by the Scientific Committee. However, many political concessions were made during negotiations, including reducing the proposed protected area by more than 40%.
These and other compromises could undermine the objectives of the MPA, which are to conserve marine living resources, maintain ecosystem structure and function, and protect vital ecosystem processes and areas of ecological significance while promoting scientific research and allowing for a commercially viable toothfish fishery.
What ASOC is doing
ROSS SEA region MPA
ASOC continues to participate in annual CCAMLR meetings, where we advocate for the highest levels of environmental protection for the Southern Ocean.
To ensure the Ross Sea Region MPA is effective, CCAMLR must implement a program of scientific research and monitoring by formally adopting the Ross Sea region Research and Monitoring plan (RMP). The RMP will provide data on the effectiveness of the MPA, which can be measured against the objectives of the MPA: protecting the Ross Sea, mitigating threats, and supporting research into the effects of fishing, environmental variability and climate change on Antarctic marine living resources.
ASOC urges CCAMLR to formally adopt the Research and Monitoring plan, and encourages all CCAMLR Members to contribute to its implementation.
What’s next?
ROSS SEA region MPA
The Ross Sea Region MPA is a success for the conservation community, but this is only the beginning. CCAMLR has been working towards creating a representative system of MPAs around Antarctica since 2002. In 2009, all Members made a formal agreement to realize this network by 2012. Despite the efforts of many Members, this deadline has long since passed.
To date only two marine protected areas, covering 5% of the Southern Ocean, have been established. These are the South Orkney Islands Southern Shelf MPA (2009), the first international MPA to be established on the high seas, and the Ross Sea Region MPA (2016).
Support ASOC as we call on CCAMLR to deliver on its word and establish the marine reserves needed to safeguard the Southern Ocean.
Ross Sea Region MPA
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES
Keep learning about Antarctic marine protected areas, and how you can call on CCAMLR to fulfill their commitment and create a representative system of MPAs around Antarctica.
 ASOC
ASOC